14 Symbols of GD&T (Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing) with PDF Guide
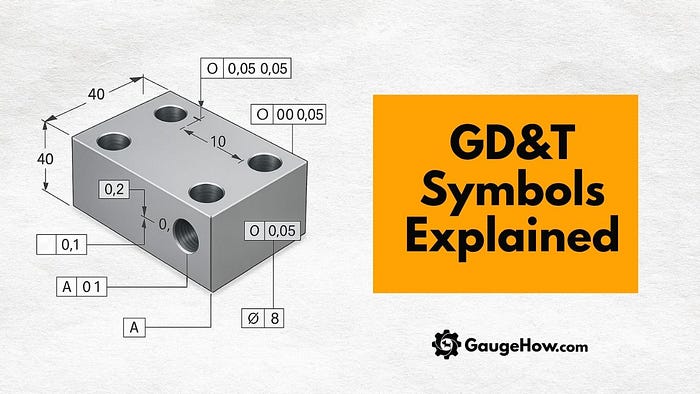
GD&T Symbols are often called the language of mechanical design. For engineers and manufacturers, they act as universal signs that say exactly how a part should be built, measured, and fitted into assembly. Without GD&T, design intent can get lost between teams, suppliers, and even countries. So let’s go step by step and understand these 14 symbols, their meaning, and why learning GD&T is one of the most important skills for a design engineer.
What is GD&T?
GD&T stands for Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing. In simple words, it is a standard way to describe the form, size, orientation and position of mechanical parts. Think of it like a contract between design engineers and manufacturers. Instead of writing long notes, symbols provide clean, sharp communication.
- Why it matters? Because if two suppliers make the same part using GD&T, both will deliver consistent results. No guesswork, no messy communication.
- It is governed by ASME Y14.5 standard.
You can think of GD&T as clear instructions for manufacturing that prevent misunderstandings and make sure parts fit together perfectly.
Common GD&T Symbols Explained
1. Straightness (―)
Controls the allowable variation of a line element or axis. Simply ensures a feature stays inside a straight-line tolerance zone.
2. Flatness (▱)
Defines the tolerance between two parallel planes. Entire surface must lie inside this zone.
3. Circularity (○)
Checks how closely a cross-section of a part matches a perfect circle.
4. Cylindricity (⌭)
Total control of a cylindrical surface. Combines circularity and straightness.
5. Profile of a Line (⌒)
Specifies variations allowed along a line or curve in 2D.
6. Profile of a Surface (⌓)
Controls shape and orientation in 3D, applied to surfaces.
7. Parallelism (∥)
Makes sure two surfaces/axes remain equidistant at all points.
8. Perpendicularity (⊥)
Defines a 90-degree orientation. Crucial in assembly fits.
9. Angularity (∠)
Controls any specific angle other than 90°.
10. Position (⌖)
Specifies exact permissible location for a feature, usually holes or pins.
11. Concentricity (◎)
Controls the center alignment of cylindrical features.
12. Symmetry (≡)
Ensures features are mirrored across a central plane or axis.
13. Circular Runout (↻)
Controls variation in circularity and axis alignment for rotating parts.
14. Total Runout (⟳)
Combines circularity, straightness, taper variation across entire rotating surface.
ASME Y14.5–2018 Update
The ASME standard earlier had all 14 symbols. But in the 2018 update, concentricity and symmetry were withdrawn from common use. Why? Because they were harder to inspect practically, and industry preferred position tolerance instead.
Still, all the other 12 remain essential and are widely applied in industries like aerospace, automotive, heavy machinery, and robotics.

Why Should Engineers Use GD&T?
- Clear Communication — prevents confusion across teams.
- Cost Savings — reduces wastage in machining and inspection.
- Improved Quality — ensures parts meet the specification.
- Interchangeability — parts made in different locations still fit perfectly.
For anyone planning to become a design engineer, knowing GD&T is not optional, it’s mandatory.
Beyond GD&T — Modern Engineering Skills
Learning GD&T is only one step. Modern engineers are expected to have a set of hybrid skills that combine design, CAD, programming, and automation.
- One must explore AutoCAD for Mechanical Engineers because CAD is the backbone of design communication. Without CAD, applying GD&T becomes difficult.
- If you’re a student or professional looking to boost your career, consider mechanical engineering certification. Certifications add credibility and help in job placements.
- Don’t just stick to drafting. Learn programming too. Python for Mechanical Engineers is a course that shows how automation and coding can simplify mechanical calculations, robotics, and simulations.
- Also, if you are aiming for a career as a design engineer, check out curated design engineer courses that give a deeper view into GD&T, CAD, and tolerance analysis.
All these courses are part of broader Mechanical Engineering Online Courses that platforms like Gaugehow offer.

How to Learn GD&T Effectively
- Start Small — Begin with the meaning of each symbol.
- Practice with CAD — Apply GD&T on simple CAD models.
- Check Industry Drawings — Compare real-world drawings with GD&T symbols.
- Get Certified — Enroll in structured programs from Gaugehow or other industry platforms.
Real-World Applications of GD&T
- Automobile Industry — Position tolerance ensures engine holes align with bolts.
- Aerospace — Cylindricity controls ensure rotating shafts remain vibration-free.
- Medical Devices — Runout tolerances ensure smooth, precise movements.
Imagine making a car engine without GD&T — every supplier would deliver slightly different fits. The engine would never run smoothly. That’s the power of GD&T.
Gaugehow and Your Learning Path
If you are serious about upgrading your skills, Gaugehow is a place worth exploring. They have 30+ specialized courses designed for mechanical engineers. From GD&T basics to Python for Mechanical Engineers, from AutoCAD for Mechanical Engineers to industry-recognized certifications — everything is structured and easy to follow.
The best part? Courses are self-paced, affordable, and focused on real-world applications rather than just theory.
Conclusion
GD&T is more than just symbols — it’s a professional language that unites design and manufacturing. Knowing these 14 symbols not only improves your technical skills but also prepares you for industry jobs where precision is everything.
But the journey doesn’t stop at GD&T. Expanding into CAD, programming, and certifications will make you stand out in this competitive engineering world. Platforms like Gaugehow give engineers exactly what they need: practical, industry-ready learning.
So whether you are a student trying to crack interviews, a professional aiming for promotions, or a curious learner who loves design — GD&T is a must, and learning it with the right mix of modern skills will make your engineering career future-proof.
Details
Visit us : Deepak S. Choudhary (Founder ) Working from workspace: Incuspaze, Vijay nagar, Indore, Madhya Pradesh, India, 452001
Contact: +919685671890
Email: info@gaugehow.com
Website: https://gaugehow.com/
.jpeg)
Comments
Post a Comment